반응형
기본 환경: IDE: VS code, Language: Python
Perceptron

: 다수의 입력으로부터 하나의 결과를 내보내는 알고리즘
: x-입력값, w-가중치, y-출력값
1. 단층 퍼셉트론(SingleLayer Perceptron)

: 1개의 입력층과 1개의 출력층으로 이뤄진 퍼셉트론
: AND, NAND, OR 회로 구현은 가능하지만, XOR 구현이 불가
AND 회로




❓ 1개의 직선(단층 퍼셉트론)은 XOR 회로 생성 불가
❗ 2개 이상의 직선을 구현하는 다층 퍼셉트론으로 XOR 회로 생성 가능
2. 다층 퍼셉트론(MultiLayer Perceptron)
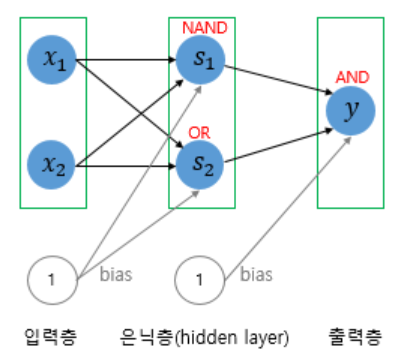
: 1개의 입력층, 1개의 출력층 그리고 입력층과 출력층 사이의 은닉층(Hidden Layer)으로 이뤄진 퍼셉트론
: NAND, OR, AND의 조합으로 XOR 구현
: 은닉층이 2개 이상인 신경망을 심층 신경망(Deep Neural Network, DNN)이라고 함
Hidden Layer가 2개 이상인 MLP, DNN 모델 만들기
# multiLayer_Perceptron.py
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
# 1. Data
x = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.4]]) # input_dim = 10(행렬에서 열 기준)
# np.array([[element1], [element2]]): 다중 배열을 만들 경우, element1과 element2의 개수를 일치 시켜야 함
y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20]) # output_dim = 1
print(x.shape) # (2, 10)
print(y.shape) # (10, )
# Data.shape: (행: 데이터 개수, 열: 데이터 요소)
x = x.T
# Data.T 행렬 전환
print(x.shape) # (10, 2)
'''
x = np.array([1,1],
[2,1],
[3,1],
[4,1],
[5,2],
[6,1.3],
[7,1.4],
[8,1.5],
[9, 1.6],
[10, 1.4])
'''
# 2. Model
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(32, input_dim=2))
# input_dim = 2 (입력값 기준으로 열의 개수, Input Layer), output = 32(Hidden layer로 임의값 설정 가능)
model.add(Dense(32))
model.add(Dense(16))
model.add(Dense(8))
model.add(Dense(1))
# output_dim = 1 (출력값 기준으로 열의 개수, Output Layer)
# 3. Compile
model.compile(loss='mae', optimizer='adam')
model.fit(x, y, epochs=100, batch_size=1)
# 4. Evaluate and Predict
loss = model.evaluate(x, y)
print("loss: ", loss)
result = model.predict([[10, 1.4]])
# predict(x1, x2)에서 x2 값을 알 수 없으므로 우선 훈련값(x1, x2)을 넣어서 y와 유사한지 확인
print("[10, 1.4] result: ", result)
'''
Result
Train(Fit)
Epoch 100/100
10/10 [==============================] - 0s 667us/step - loss: 0.0817
Evaluate
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 98ms/step - loss: 0.1372
Predict
[10, 1.4] result: [[19.758385]]
'''
➕ Model Summary 확인
# summary.py
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
# 1. Data
x = np.array([1,2,3])
y = np.array([1,2,3])
# 2. Model Instruction
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(5, input_dim=1))
model.add(Dense(4))
model.add(Dense(3))
model.add(Dense(2))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.summary()
'''
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape(노드의 개수) Param #
- model.add(Dense(*)) parameter (연산): node + bias -> 실질적으로는 node+1이 됨
=================================================================
dense (Dense) (None, 5) (data 개수, node 개수) 10 (2*5)
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 4) 24 (6*4)
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 3) 15 (5*3)
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 2) 8 (4*2)
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 1) 3 (3*1)
=================================================================
Total params: 60
Trainable params: 60 -> 훈련이 필요한 나의 model에 대해서는 훈련이 필요
Non-trainable params: 0 -> 이미 훈련된 남의 model에 대해서는 훈련이 따로 필요없으므로 non-trainable에 사용
_________________________________________________________________
'''
⭐ Summary Node 보충 설명

소스 코드
참고 자료
반응형
'Naver Clould with BitCamp > Aartificial Intelligence' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Split training data and test data (0) | 2023.01.21 |
|---|---|
| Scalar, Vector, Matirx, Tensor (0) | 2023.01.20 |
| Hyper-parameter Tuning (0) | 2023.01.20 |
| Types of Artificial Neural Networks (0) | 2023.01.15 |
| ANN Model Construction (0) | 2023.01.15 |